Google sees a total of 3.5 billion searches every day. The question is, how can you rank on page one of the search results to take advantage of some of that traffic?
The best way to go about it is with SEO optimization. If you want to optimize your SEO blog post today, you’ll need to use structured data.
This guide will explain what structured data is and how you can include it in your SEO blog writing strategy.
What Is Structured Data?
Structured data for blog posts, or schema markup, is markup code that gives search engines information about your website. It helps search engine crawlers understand the purpose of your content and learn more about specific elements of your pages.
Think of things like your article author, publish date, and page title. Structured data will tell Google what those things are so it doesn’t have to guess. If you have more advanced content types like reviews, event dates, or questions and answers, Google provides structured data fields specifically for that content.
You can also use structured data to improve your search engine listing. Structured data tags can add review stars, jump links, prices, and breadcrumbs directly on the search results.
How Do You Add Structured Data to Blog Posts?
If you use a popular website platform like WordPress, you’ll have plugin options that will do this for you automatically. Yoast SEO, for instance, adds fields inside your WordPress pages and posts that let you tag all the data you need.
If you don’t have a plugin to handle structured data, you still have options. Google provides an easy-to-use tool called the Structured Data Markup Helper to assist with your blog post structured data.
Schema markup for blog posts sounds like a complex topic at first. The good news is that it isn’t difficult to add it to your SEO blog writing process.
Using the Structured Data Markup Helper
When you first load the structured data markup helper, you’ll see a list of post types. Think about your post and the type of content you’ll show your visitors. Since we’re marking up a blog post in this example, click on the “Articles” option.
Once you select the article type, enter the URL for your web page and click on “start tagging.” Alternatively, you can use your page HTML if it’s available to you. The next page you’ll see will contain your website in visual form. From here, you can start marking up your page.
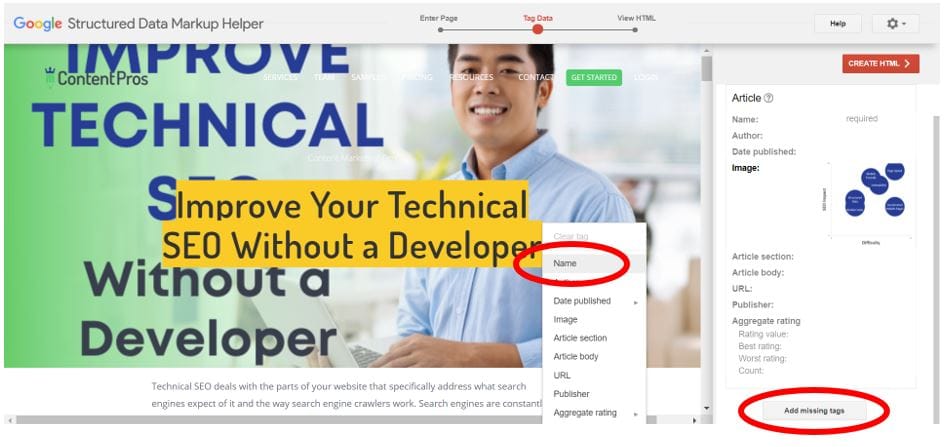
The most critical element to tag is the name. It tells Google your page title and is required to have a valid schema. Highlight your page title to select it and click the “Name” property on the popup that appears.
After you mark your name, look at the rest of your options on the right side of the window to see what else is available. Some standard schema options are “date published,” “author,” “publisher,” and “URL.” Highlight them in your text to add them to your schema. If they aren’t available in your page text, click on “add missing tags” on the right to add those options manually.
Once you finish tagging your blog post, you’re ready to get your schema data for blog posts. Click on the “CREATE HTML” button in the top right of the screen to get your output. You’ll receive code in JSON-LD format. Copy your JSON-LD code and add it to the header on your blog page. You can also use this code as a structured data example to quickly add to your other pages so you don’t have to repeat this process for every page.
If you don’t have direct access to your website code, you’ll need to add this code to the HTML editor in your content management system. Most editors have a visual editor and an HTML editor. Switch to the HTML version to add your code.
Start Adding Structured Data to Your SEO Blog Posts
As you can see, it doesn’t take much to add blog post structured data. Keep in mind, though, that this guide only covers the basic elements. There are more ways to add structured data to blog posts, so make sure to check out other structured data examples to learn what else you can do.
Once you nail your schema markup for blog posts, you can start working on other technical SEO work for your site.