The first three days of our nine-day plan to SEO success focused mostly on learning SEO principles and auditing techniques – which are important! Now, it’s time to deploy your new knowledge and skills to create a great user experience for your website visitors.
On-Page SEO: Page and Content Optimization, URL Optimization, Links, and Images
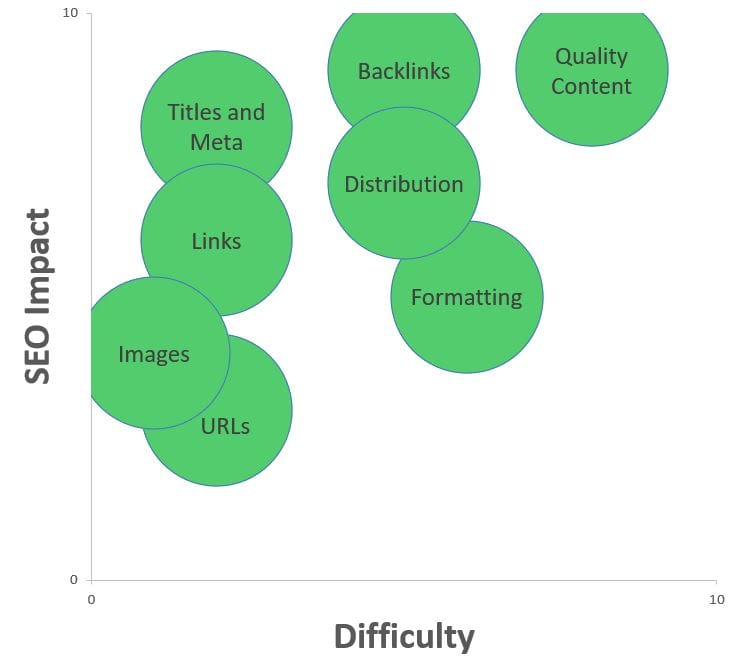
Let’s start by covering the major points you’ll want to audit first and why they matter:
1. Content Quality
High-quality content will do more for SEO than any other single factor. The majority of ranking factors that search engines use to rank websites look for indicators of content quality.
You already know that dwell time, backlinks, and tons of other factors have a powerful impact on SEO performance. Your content is the main thing that will keep visitors clicking on your website and convince other website owners to link to you.
When optimizing on-page content, think beyond the simple task of advertising a product or service. Consider how you can use text, imagery, and video to create a valuable experience for users.
Try structuring each page to answer a single question that users might have. This ensures that people who click onto your website obtain information that is relevant to the problems they want to solve. Consider the buyer personas you created when reviewing content and ask yourself if your content would meet those peoples’ needs adequately.
2. Page Titles and Meta Descriptions
Your page titles and meta descriptions should reflect the value of the page they represent. That means they should directly address the problems your product or service promises to solve.
They should also include your keywords, along with related terms and phrases that point to your web content’s specific value.
These small snippets of information go a long way towards obtaining and maintaining top search engine rankings. Since they are among the first pieces of content your users read, they need to be compelling and unique. This is your first chance to stand out from the crowd.
To write great page titles and meta descriptions, you must learn how to do more with less. You must find a way to pique users’ curiosity and engage them without going over strict character limits:
- Page titles should have between 30 and 60 characters.
- The best-performing meta descriptions have at least 70 characters and less than 130. The absolute maximum is 160 characters!
To get an idea of what you’re working with, the first bullet point above has 53 characters. The second one has 124.
You don’t have much space to work with. Incorporate your most valuable selling points and summarize – without deception – the subject of the page you’re introducing. Be sure to include action verbs or psychological “trigger words” that compel readers to act.
Examples of trigger words that perform well in page titles and meta descriptions include:
- Find out
- Discover
- Proven
- Exclusive
- Free
- Hurry
Each of these trigger words carries a slightly different message. Make sure your page titles and meta descriptions tell users to do the right thing based on their current place in the sales funnel. “Finding out” about something is good for building awareness, while telling visitors to “hurry” means you want them to make a purchase now!

©pixelcreatures via Canva.com
3. Headings Structure and Content Formatting
The next part of your website to pay attention to is its heading structure and format. Headings help divide web pages into easily readable sections of content. Without them, your website will look like a 19th-century university textbook – giant blocks of text on every page.
Readability isn’t the only reason you should update your heading structure and formatting, though. Taking an SEO-oriented approach to the way you organize text can help you attain one of Google’s most valuable prizes: a Featured Snippet.
You’ve probably already seen Google’s media-rich snippets in action. If you search for a high-value key phrase, and Google finds a highly structured response to your question on one of its indexed websites, it might show you that information right on the results page. This eye-catching response can put you above the #1 ranking position instantly!
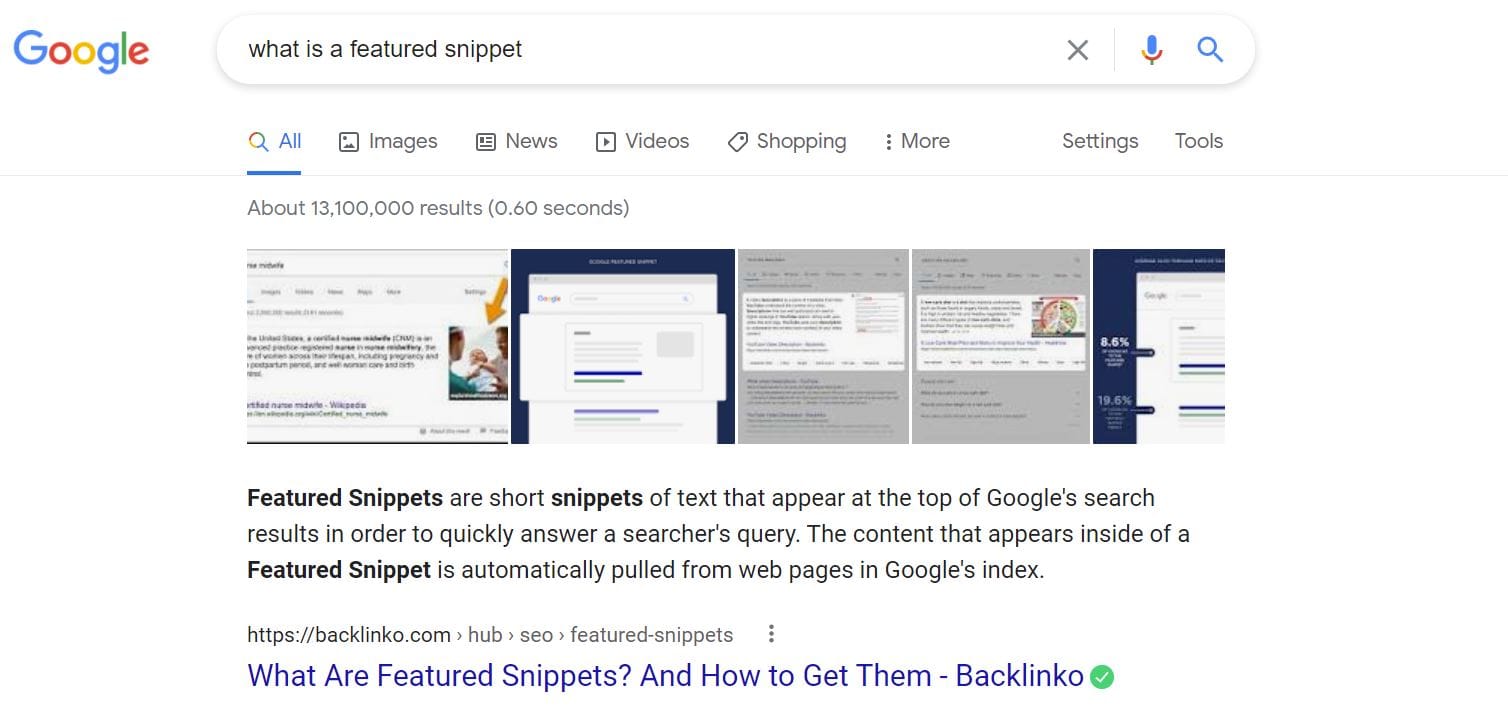
Google has multiple kinds of snippets. You should identify core value statements in your content and structure them as answers to the questions that users will ask on Google. The three major kinds of format structures Google snippets have are:
- Paragraphs. By far the most common type of snippet, Google’s paragraph snippets answer user questions in 40-50 words (or about 300 characters). Including a search query keyword in a header title and writing a quick, snippet-ready answer beneath is the best way to get a coveted paragraph snippet.
- Lists. Lists are less common than paragraphs but frequently show up when users search for “prices” and “comparisons.” Google is looking for well-structured, number-driven content here, and its crawlers will pick up any relevant data that is organized using bullet points, numbered lists, or a similar format.
- Tables. Google will sometimes treat its users to a fully sortable, dynamic table with a chart included. This typically happens when users search for information in an “x by y” format. For instance, “2016 car sales by brand.” In this case, it’s important to title your table using the same pattern so that Google knows what to look for and how to present the data.
Once you have your content formatted, structured, and properly defined, you’re halfway through on-page SEO. We can now move to more technical parts of your on-page SEO assets. This will prepare you to move onto the purely technical territory of off-page SEO in the following days.
4. URL Optimization
Search engines simply don’t like long, complicated URLs. The way your website’s various pages are structured can make a major difference in the way search engines perceive their value. Your URLs say a lot about the way your website is structured.
Short URLs show website visitors and search engines exactly what each individual page is about. Long URLs are typically filled with ugly valuable structural code that gets in the way of website visitors’ user experience. Web pages with shorter URLs get shared on social media more often, and users are more likely to immediately understand and trust where they are going if they can read the URL.
URLs should point towards the subject of the web page in human-readable, hyphenated format. A URL like https://www.example.com/shop/brown-shoes.html is far better than https://www.example.com/index.php?idsezione=360%sid=3a5ebc9441fdaa6fbf314529535864. Neither a human user nor a web crawler can easily make sense of what the latter webpage is supposed to offer.
Important: Google prefers hyphens to spaces and underscores in web URLs. Don’t use anything other than hyphens to separate words in URLs.
5. Internal and External Links
Your links play an important role in your website’s overall SEO performance. For the best results, make sure your website includes a healthy number of internal and external links placed in the appropriate places to build credibility and authority.
- Internal links direct users to other pages on your own website. They make it easier for search engines to correctly index web pages, and they give users easy access to contextual navigation.
- External links direct users to pages located on other websites. Search engines will use these links to determine how authoritative and trustworthy your content is. Linking to high Domain Authority websites in your field will convince search engine algorithms to rank your pages higher.
Of course, if any links on your web pages are broken, you’ll want to fix those right away. Most search engines will forgive a few 404 errors on an otherwise high-quality website, but having too many will negatively impact the user experience.
Most often, links break because the destination domain’s site owner changed the URL. If your website has too many outgoing links to verify manually, you can use a tool like Ahref’s free site audit to find out exactly where they are.
This tool will also tell you if you have broken links incoming from other websites. On Day 6, we’ll cover exactly what to do when someone links to your domain but gets the URL wrong.
6. SEO Images
Images are incredibly important communication tools. A high-quality visual can considerably boost the SEO performance of a page, especially if it’s properly tagged.
If you have blog posts, product pages, and other website assets that don’t include images, the first step is finding great images to add. Free Creative Commons images available on websites like Pixabay and Unsplash can improve user engagement and give search engines a far better idea of your website’s value.
Well-designed stock imagery helps reinforce the value your website content communicates. An attractive, well-structured web page will engage users far better than a big block of text.

©atakan via Canva.com
7. File Names, Formats, and Captions
Image SEO depends heavily on the file name you give your image. You want to tell search engines what the image is of and demonstrate the value of that image to an automated web crawler that may not be able to see it.
By default, most images on Unsplash are named after the image author, with a string of characters and the website name attached. “melanie-karrer-T1jw85v_2SE-unsplash” is not a very SEO-friendly filename. “Dolomite-mountains-South-Tyrol-Italy.jpg” is simpler and more descriptive.
Don’t try to force keywords and phrases into the image filename unnaturally. It’s great if they happen to match up (like a postcard view of an Italian mountainscape for a travel blog about Italy, for instance), but including keywords unnaturally will hurt SEO more than it will help it.
Next, you should select the appropriate image file format. The four most popular use cases and formats you should be aware of are:
- JPEG for large photos and illustrations. These are high-quality images that can load quickly.
- PNG for vector drawings and illustrations you want to layer over a background. This image format preserves background transparency.
- WebP when you have large numbers of images dragging down page load speed. It’s designed to maximize image compression without ruining image quality in the process.
- SVG for logos, icons, and other small images. Web developers typically manage small images in SVG format so they can easily manipulate them in CSS or JavaScript.
The final step you’ll want to take is to make sure your major images have alt-text titles and captions. These will replace the images when users can’t load or view the images themselves. Importantly, they will also inform web crawlers what the image depicts. These should be as short and descriptive as the image’s filename. It’s rarely necessary to be extremely specific with alt-text.
At this point, your SEO strategy is almost entirely in place. Now, all you need to do is make sure your content is reaching the people it should be. The way you promote your website will hugely influence its overall SEO success.
©kemalbas via Canva.com
8. Off-Page SEO: Website Promotion and Backlinks
Backlinks are among the most valuable ranking factors that search engines look for when indexing pages. Earning multiple backlinks from high Domain Authority websites is by far the fastest, most effective way to improve page ranking.
But you can’t just ask for backlinks. You can’t buy them either – although plenty of people try. The only legitimate way to earn longtime value from high-authority backlinks is by making and distributing great content to the right people.
Distribute your content well, and it will get to the right people. There are several ways you can help that process along:
- Guest Blogging. Writing for other websites (and inviting people to write for yours) is one of the best ways to get high-quality content and backlinks on your site. It raises awareness of your brand and boosts its credibility while guaranteeing exposure to new audiences.
- Social Media. Facebook, LinkedIn, Twitter, YouTube, and Quora are all valuable backlink-generating platforms. These links matter especially when they come from other peoples’ pages and posts. Social media is the perfect platform for reaching out to bloggers, journalists, and influencers who have an impact on your field.
- Email Newsletters. Email doesn’t directly impact SEO, but it drives qualified traffic to your website, improves on-site engagement, and encourages social sharing – all of which will help you promote your best content and earn valuable backlinks.
By promoting your content consistently, you ensure that your valuable content reaches the people who need to see it. The more accessible your content is for them, the better your results will be in the long term.
That Wraps Up Basic SEO – Now It’s Time for the Advanced Stuff
Optimizing your content, imagery, and links for search engine ranking is the first step towards SEO success. Your website should now be a valuable resource for users and customers, with content that addresses peoples’ needs and keeps them coming back for more.
Although optimal content is the cornerstone of a good SEO strategy, it’s not the only thing that matters. There are dozens of technical parameters that search engines use to distinguish between good websites and bad ones. The next steps of your SEO journey will take you through some of these and the technology that underlies them.
Technical SEO might sound intimidating, but there are lots of things you can do to improve your website’s ranking without any technical expertise at all. Our 4-day guide to advanced SEO is dedicated to technical optimization, off-page SEO techniques, and attribution strategy. Read Part Two of our comprehensive guide to SEO to get started!

